Lack of sex-disaggregated data and other gender-related gaps in Indian government’s official data sources is making it difficult to track issues such as girls’ and women’s employment, asset ownership, health, sanitation and education. This results in a limited understanding of gender issues and poorly designed policies and programmes. As part of their Data Gaps series, IWWAGE’s second story examines which women-specific data points are not collated or made public, and how this makes women invisible and hinders progress towards gender-equality goals. Read the article here.
Category: Research and Impact
LEAD’s research proposal shortlisted by Dvara Research
Researchers from LEAD at Krea University presented findings from their ongoing research at the Dvara Research’s Household Finance Research Roundtable. The study, one of the 10 research proposals selected by Dvara, seeks to identify and understand factors that influence financial decision-making through a migration lens.
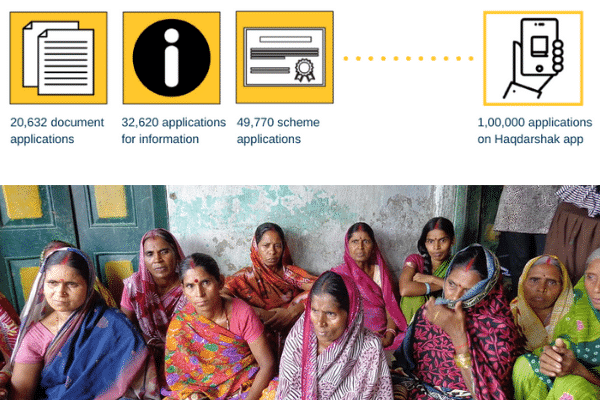
IWWAGE-Haqdarshak project receives 100,000 applications
Over 100,000 applications were received in Chhattisgarh through a digital solution to deliver government entitlements. The project is being implemented by the Initiative for What Works to Advance Women and Girls in the Economy (IWWAGE) and Haqdarshak Empowerment Solutions, with support from the Chhattisgarh SRLM. Anoushaka Chandrashekar and Raka De from LEAD reflect on this tremendous milestone here.
IWWAGE report on women SHGs & NRLMS during COVID-19
Women’s SHGs of NRLM emerged as pivotal actors in crisis management, leading from the front in – producing masks and protective gear, creating awareness about the pandemic, delivering essential goods and financial services to the most vulnerable and running community kitchens. Read IWWAGE’s insightful report on the community and institutional response to COVID-19 in India here.
IWWAGE is partnering with DAY-NRLM through SWAYAM
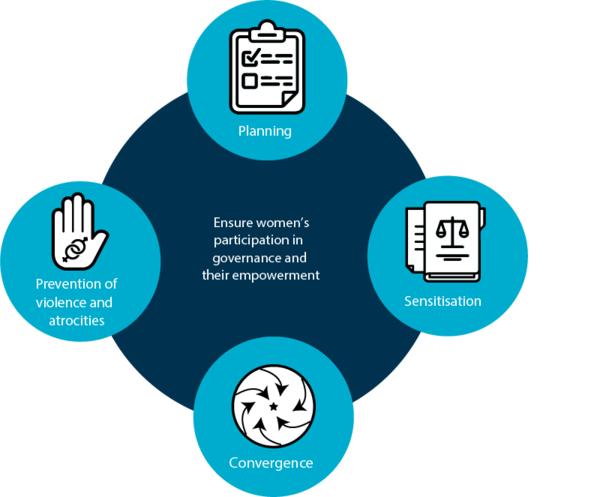
With over 60 million women mobilised to be part of one of India’s largest livelihoods programme, the Deendayal Antayodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM), holds great promise for advancing women’s socio-economic empowerment by organising them into self-help groups (SHGs) and institutions of the rural poor. These platforms are facilitating financial opportunities and livelihood support services for women. NRLM believes that gender sensitisation and social action should be mainstreamed in its framework, systems, institutions and processes. To this end, it devised a Gender Operational Strategy in financial year 2019-20 committing actions that recognise women’s heterogeneity and the unique socio-economic barriers faced by them.
Through SWAYAM (Strengthening Women’s institutions for Agency and Empowerment), IWWAGE is partnering with DAY-NRLM to provide technical assistance to support this strategy and institutionalise gender across all levels of the Mission. More specifically, the partnership aims to:
- Strengthen capacity of staff at all levels in the NRLM through trainings to work on gender issues;
- Redesign the existing gender training curriculum used by State Rural Livelihood Missions;
- Design and test innovative solutions for delivering the trainings;
- Design, implement and evaluate the impact of pilot Gender Resource Centres in four states as models to promote gender equality and help women claim their entitlements; and
- Build performance indicators, generate rigorous evidence and develop knowledge management mechanisms to inform programme design.
IWWAGE is partnering with SRLMs in four states including Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand and Odisha, and several implementing partners to test pilots and scale these institutional models for SHG federations to serve as gender resource centres. Read more on IWWAGE work with NRLM here.
Women’s Work Force Participation in Maharashtra
Women’s labourforce participation rates (LFPR) reveals some interesting trends for Maharashtra. As per the figures from the labourforce surveys, the LFPR is significantly higher than the all-India figures, largely driven by higher than average rural employment. The state also shares a decline in self-employment and casual employment and a shift towards regular wage work for both rural and urban women. In Maharashtrathe urban areas witnessed a consistent rise in regular wage work of women since 2004-05. More than 60 per cent of women are employed as regular workers – 70 per cent of which is concentrated in the services sector such as education, health and retail. In rural areas, the share of casual workers is considerably higher at around 42 per cent, followed by 52 per cent in self-employment. The incidence of unpaid family workers among self-employed women exceed 80 per cent. While the urban areas show considerable diversity of women workers across occupations and sectors, women in the rural areas remain concentrated as manual workers in agriculture or within construction work.
Initiative for What Works to Advance Women and Girls in the Economy (IWWAGE), has developed a series of factsheet that highlight the important aspects of women’s employment across the states in India. It uses secondary data provided by the National Sample Surveys’ Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS), 2017-18, and the employment-unemployment surveys (EUS) as well as data from other sources to support state specific analysis. The Maharashtra factsheet is part of this series, and can be accessed here.
IWWAGE launches ‘Gender in Focus’ Magazine
IWWAGE, an initiative of LEAD at Krea University, launched the first edition of its quarterly Magazine, Gender in Focus. The digital magazine showcases IWWAGE’s work in the intervention, research and advocacy space around key issues emerging as challenges for women’s economic empowerment in India. Gender in Focus presents a teaser of some of the work that IWWAGE is involved in, to address some of these challenges and in capturing best practices.
The inaugural issue brought voices from the field based on open-ended discussions held with our partner civil society organisations in four states, on how women and their groups have been affected by the pandemic and the lockdown. In addition, the issue provides snapshots of webinars conducted around the theme of COVID-19 and its impacts on women in different domains, and presents a new series of policy notes, to provide timely and actionable recommendations so that policies or programmes announced by governments help build not only a more resilient, but a gender responsive world post COVID. Besides the emphasis on COVID, this Gender in Focus issue presents summaries of the other exciting work that IWWAGE has been engaged in, such as, unpacking state-wise trends in labour force participation in India, the sectors that women work in and wage gaps; a new policy and programme series (also at the state level) to map what programmes exist and are targeted at women, and their effectiveness; women’s engagement with the gig economy and the precariousness they face while engaging with such platforms; and digital solutions that IWWAGE is working on with its tech partners in helping women gain information about their rights and entitlements. Gender in Focus can be downloaded from the website with this link- Gender in Focus.